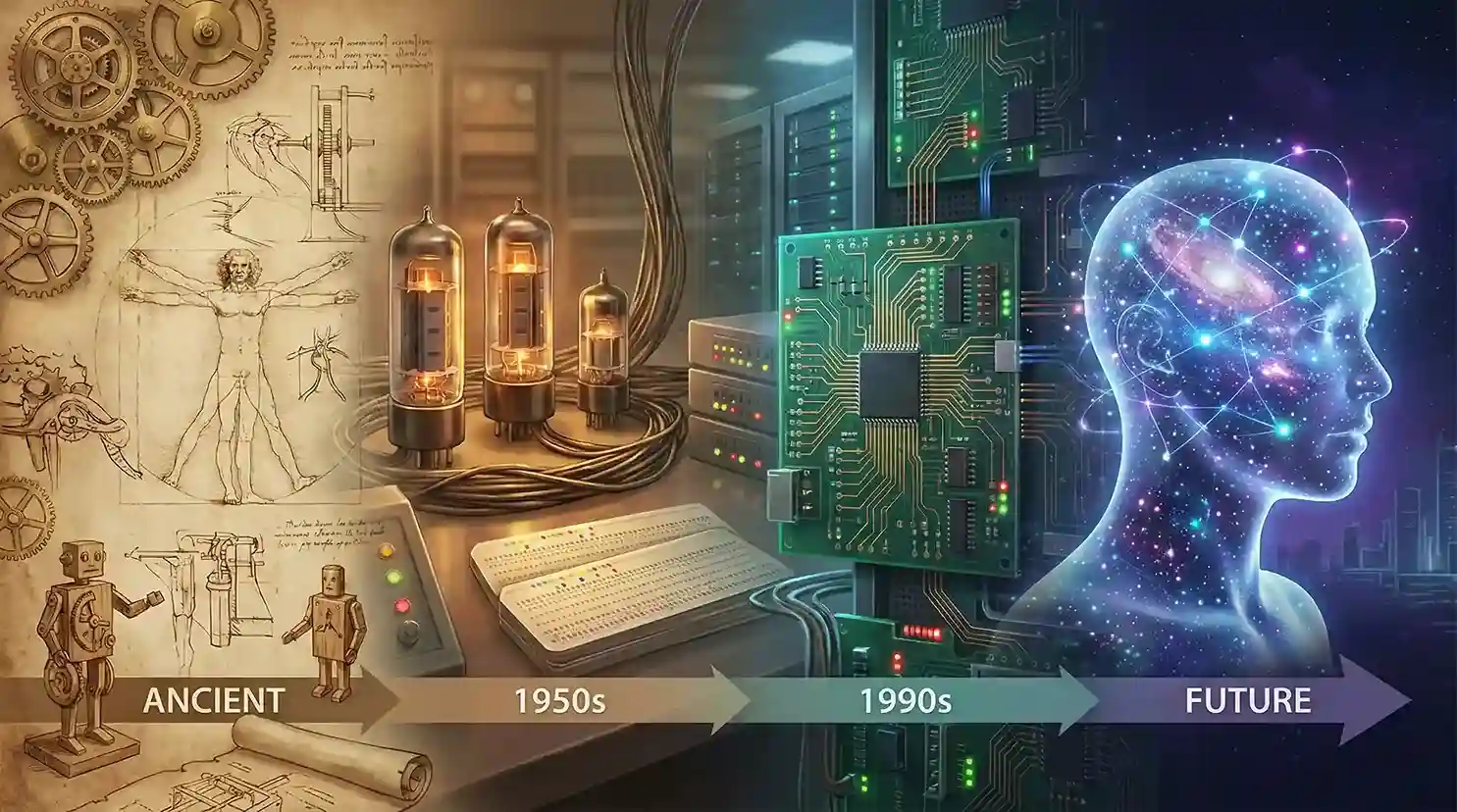
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is everywhere today—powering recommendation engines, self-driving cars, chatbots, voice assistants, medical analysis tools, and more. But one question still confuses many people:
How was AI discovered?
Was it invented suddenly? Did one scientist create it? Or did it evolve over time?
In reality, AI was not discovered overnight. It emerged through decades of research in mathematics, computer science, psychology, neurology, and engineering. This article breaks down the complete journey of AI in an easy-to-understand way—perfect for beginners, tech lovers, and curious readers.
The Early Origins: Before The Term “AI” Even Existed
Long before computers existed, early philosophers wondered:
- How does the human mind think?
- Can reasoning be turned into rules or math?
- Can machines imitate intelligence?
H2: Ancient Ideas That Inspired AI
Some of the earliest inspirations for AI came from:
- Aristotle’s logic (300 BC) – He created rules for reasoning, which later influenced computer algorithms.
- Automata and mechanical machines – Ancient engineers built self-operating devices that sparked the idea of artificial “life.”
- Mathematics of logic – In the 1800s, George Boole invented Boolean logic, the foundation of computer circuits.
These ideas set the stage—but AI still needed one crucial invention.
The Birth of Computing: The Foundation of AI
AI truly became possible only when computers arrived.
H2: Alan Turing – The Mind Behind Machine Intelligence
In 1950, mathematician Alan Turing published “Computing Machinery and Intelligence.”
He asked the famous question:
“Can machines think?”
Turing also created the Turing Test, a method to check if a machine’s responses could fool humans into thinking it’s human.
This is widely considered the birth of modern AI thinking.
The Moment AI Was “Officially” Born: 1956 Dartmouth Workshop
H2: The Event That Created AI as a Field
In 1956, at Dartmouth College, a group of scientists met for a special research project. This moment is known as the official birth of Artificial Intelligence.
The team included:
- John McCarthy
- Marvin Minsky
- Allen Newell
- Herbert Simon
John McCarthy also coined the term “Artificial Intelligence.”
Their goal?
To build machines that can learn, reason, and understand like humans.
This workshop launched AI as a dedicated scientific field.
The First AI Programs: Logic, Reasoning & Games
H2: Early AI Achievements
Between the 1950s and 1970s, researchers created AI programs that could:
- Solve math problems
- Play chess and checkers
- Understand simple language
- Prove logical theorems
Examples include:
- Logic Theorist (1955) – The first AI program
- ELIZA (1966) – A chat-like program that mimicked a therapist
- Shakey the Robot (1969) – The first robot that could make decisions
These programs were simple but groundbreaking.
AI Winters: When AI Nearly Failed
AI progress slowed down twice—in the 1970s and late 1980s.
H2: Why AI Struggled
- Computers were too slow
- Not enough data
- Expectations were unrealistic
- Funding dropped
These periods are known as AI Winters, when research nearly stopped.
But AI made a comeback thanks to one powerful idea.
The Rise of Machine Learning: The Turning Point
The 1990s and early 2000s brought a major shift. Instead of hardcoding rules, scientists created systems that learn from data.
H2: What Made Machine Learning Powerful?
- Faster computers
- Huge datasets
- Better algorithms
- Cheaper storage
This shift helped AI move from theory to real-world use.
AI now could:
- Recognize speech
- Identify images
- Predict patterns
- Improve automatically
Machine learning is the reason AI became practical.
Deep Learning Explosion: Modern AI Begins
The 2010s marked the true explosion of AI thanks to deep learning, inspired by how human brains work.
H2: Game-Changing Breakthroughs
- Neural networks started outperforming humans in image recognition
- Natural language models improved dramatically
- AI beat world champions in Go, Chess, DOTA, and Poker
- Voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant became mainstream
Deep learning enabled the creation of advanced AI models like:
- GPT (language models)
- BERT
- ResNet
- Stable Diffusion (AI image generation)
This is the AI we experience today.
H2: How AI Evolved Into Everyday Technology
Today, AI powers:
- Smartphone apps
- Self-driving cars
- Medical diagnostics
- Chatbots & customer support
- Smart home devices
- Fraud detection
- Creative tools (writing, editing, designing)
AI is no longer a research topic—it’s a technology shaping our daily lives.
FAQs
Q1: Who invented AI?
AI wasn’t invented by one person. But John McCarthy, Alan Turing, Marvin Minsky, Allen Newell, and Herbert Simon played major roles.
Q2: What year was AI created?
AI officially began in 1956 at the Dartmouth Workshop.
Q3: Why did AI suddenly become powerful?
Because of faster hardware, massive data, machine learning algorithms, and deep learning breakthroughs.
Q4: Is AI dangerous?
AI is a tool. Its impact depends on how humans design, regulate, and use it.
Q5: Will AI replace every job?
AI will automate some tasks but also create new roles. Humans and AI will likely work together.
Conclusion
AI wasn’t discovered in a single moment.
It grew from ancient logic to modern deep learning, shaped by decades of research and technological advancement. From Alan Turing’s theories to today’s intelligent systems, AI has evolved into one of the most transformative technologies of our time.